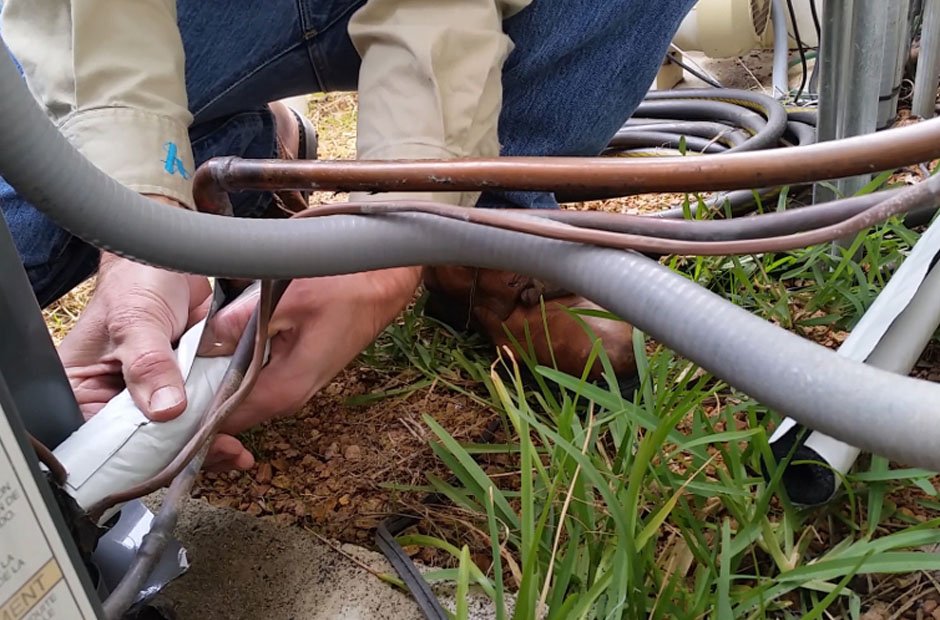
Ensuring that an HVAC system operates optimally depends significantly on the correct sizing of the line sets, notes Sand Dollar Property Management. Line sets are the copper tubing that connect the outdoor unit of an air conditioning or heat pump system to the indoor evaporator coil. They are responsible for carrying the refrigerant, which absorbs heat inside the building and releases it outside. If the line set is not appropriately sized, it can cause various issues, including decreased efficiency, increased energy consumption, and even damage to the compressor. We will explore the critical considerations for determining the correct size of HVAC line sets to maintain an efficient and well-functioning cooling system.
Understanding the Components of an HVAC Line Set
An HVAC line set consists of two primary components: the liquid and suction lines. The liquid line carries high-pressure liquid refrigerant from the outdoor unit to the indoor evaporator coil, while the suction line returns low-pressure gas refrigerant to the outdoor unit. The diameter and length of these lines must be carefully selected based on the system’s requirements. The diameter of the suction line is particularly crucial because it influences the velocity of the refrigerant and the oil return to the compressor. If the suction line is too large, the refrigerant will move too slowly, causing oil to settle in the line instead of returning to the compressor.
On the other hand, if the suction line is too small, the refrigerant will move too quickly, leading to a drop in pressure and reduced cooling efficiency. The liquid line must also be correctly sized to ensure the refrigerant is delivered to the evaporator at the correct pressure and temperature. Incorrect sizing can lead to refrigerant flash, where the liquid refrigerant turns into vapor before reaching the evaporator, significantly reducing cooling capacity.
Factors Affecting the Sizing of HVAC Line Sets
Several factors need to be considered when sizing HVAC line sets. The most critical factors include the system’s refrigerant type, capacity, and the distance between the outdoor unit and the indoor coil. Different refrigerants have varying properties, such as density and pressure, affecting the line set’s flow characteristics. For example, systems using R-410A refrigerant require more extensive suction lines than R-22 because R-410A operates at a higher pressure. The system’s capacity, measured in tons, also influences the line necessary size. Larger systems that move more refrigerant will typically need more extensive diameter lines.
Additionally, the distance between the indoor and outdoor units significantly determines the correct line size. Longer line sets increase friction loss, which can reduce the system’s efficiency. In such cases, larger diameter lines may be necessary to minimize the pressure drop. However, extending the line set beyond the manufacturer’s recommended length can introduce complexities, such as the need for additional oil traps or a larger compressor to compensate for the increased pressure loss.
The Impact of Line Set Length on Performance
The HVAC line set’s length directly impacts the cooling system’s performance and efficiency. A line set that is too long can cause a significant pressure drop, reducing the system’s capacity to cool the space effectively. This is particularly concerning in large residential or commercial installations where the indoor and outdoor units may be far apart. To mitigate these effects, installers often need to upsize the line diameter or include additional components, such as oil traps and refrigerant charge adjustments, to ensure proper operation.
Conversely, a line set that is too short can cause the refrigerant to move too quickly, which can result in noise issues, increased wear on the compressor, and potential refrigerant slugging. Manufacturers typically provide guidelines on the maximum and minimum allowable lengths for line sets, and adhering to these guidelines is essential for maintaining system efficiency and avoiding costly repairs. Properly sized line sets ensure the refrigerant moves at the correct velocity, preserving system efficiency and longevity.
Selecting the Right Line Set for Variable Speed Systems
Variable speed HVAC systems adjust their capacity based on the cooling demand and require careful consideration when sizing line sets. These systems operate across a wide range of conditions, with refrigerant flow rates that can vary significantly depending on the load. In such systems, the line set must be sized to accommodate the highest load while maintaining efficient operation at lower speeds. This often involves a more complex calculation process, as the line must be able to handle varying refrigerant velocities without compromising oil return or causing excessive pressure drops.
Additionally, using variable refrigerant flow (VRF) systems, common in commercial applications, introduces further complexity. Depending on the distance and the number of indoor units connected to the system, these systems may require different line sizes for various installation sections. Selecting the correct line size for variable speed systems is crucial to ensure the system can operate efficiently across all load conditions, avoiding issues such as compressor damage or reduced cooling capacity.
Properly sizing HVAC line sets is critical to ensuring that a cooling system operates efficiently and effectively. Incorrect sizing can lead to various issues, from reduced cooling capacity to compressor damage, resulting in higher energy costs and potential system failures. By understanding the components of the line set, considering the factors that affect sizing, and following best practices for installation, homeowners and installers can ensure that the HVAC system provides reliable and efficient cooling. We have explored the importance of selecting the correct line size, considering the system’s refrigerant type, capacity, and line set length. Additionally, we discussed the unique considerations for variable speed systems and the best practices for installation. An HVAC system can achieve optimal performance with proper attention to these details, ensuring comfort and efficiency for years.