One of the most important developments in networking that has surfaced after Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP), not an expert but ST and RST do share some similarities. Discover the major improvements of RSTP in this article and how it marks an epoch-making moment for networks. If you are a network administrator, an IT professional or just have some grounding in networking technologies then this knowledge will be absolutely essential when it comes to providing the best possible connectivity of your devices.
Basics of RSTP
But first, you need to understand the basics of RSTP before getting into improvements. Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) : In 1980s Radia Perlman developed the Spanning tree protocol, STP to reduce broadcast radiation in the ethernet network and create loop free logic topology. I nipped network loops in the bud, but it still had its slew of problems. STP definitely did not have fast convergence times. The convergence time is exactly how long the network needs to recover after a topology change such as link failure or adding of switch. Bridging loops created by L2 switches could remain primarily blocked for up to 30-50 seconds as STP converged; unacceptable in today’s high availability, low downtime networks.
This brings us to RSTP (IEEE 802.1w) – a new and improved STP, introduced in the year 2001, with improvements over most of these limitations [2]. RSTP maintains the underlying workings of STP, but adds-in several mechanisms to optimise network stability and performance.
Key Enhancements of RSTP
1. Hastened Convergence: The Sudden Death of Network Instability
Arguably the most important improvement of RSTP over STP is that it converges much faster. Convergence time is the amount of time needed for a network to return to stability after its state has been altered due to actions such as link failure, switching in of a new device or some other network reconfiguration action. Decisive in today’s networks where availability and uptime are more crucial than ever, protracted convergence times can cause significant damage when there is a failure. This issue is addressed in RSTP by some mechanisms that explain why it converges much faster than STP.
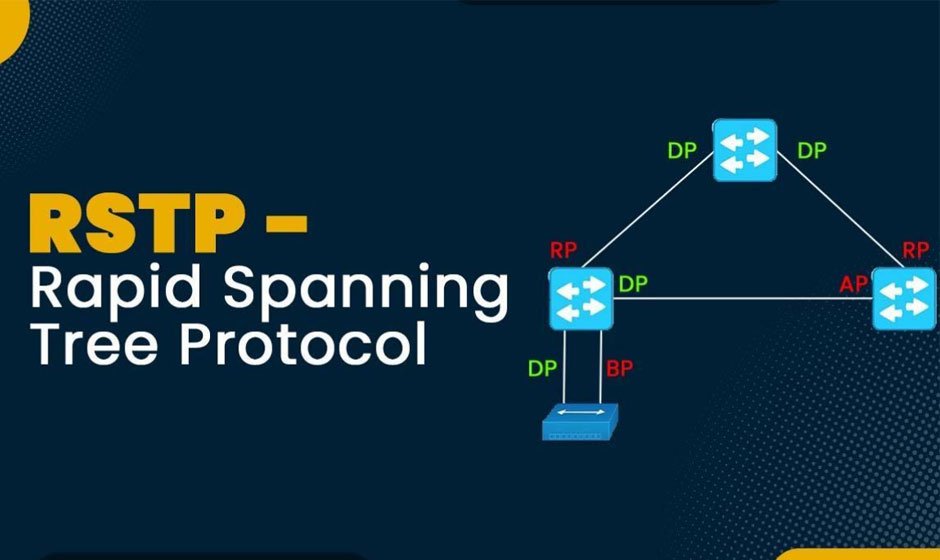
2. Streamline Network Topology Management With Port States and Roles
The Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) defines a more granular set of port states and roles to improve the accuracy with which topologies are managed, increasing network efficiency and reliability. This effectively mitigates the overhead introduced by a continuous reconfiguration of STP, and grossly simplifies worst-case operation for turning failure reaction to network-administrator interaction only.
3. Better BPDU Process: Promotes very fast network messages at scale
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol ( RSTP) is another essential enhancement, especially on the way of dealing with Bridge Protocol Data Unit messages. BPDUs play a fundamental role in the RSTP operations as they provide information needed to maintain network topology. The improvements regarding the acting of BPDU in RSTP actually grew up as enough to create a very fast converging and far more stable network.
4. Fast Forwarding State Transition: Downtime Reduction
Among the most compelling innovations achievable through use of RSTP is to have certain ports transition directly from Blocking State To Forwarding state as soon the Change has been identified, a feature which significantly reduces network downtime during topology changes. This is a huge step forward compared to traditional Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), which as many of you know requires state transitions that introduce delays and can affect network performance.
5. Optimising Network Efficiency for End Devices with Edge Ports and PortFast
RSTP introduces the concept of edge ports and integrates PortFast to make the network faster with respect to those which are hosts connected directly using these fast technologies. They are key ingredients for fast network convergence, ensuring rapid connectivity return between major connected devices like computers and printers.
6. Optimise Network Topology Changes in Link-Type Attributes
A critically important enhancement to the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) is The Link-Type attribute which assists in improving network topology change handling. RSTP does this by separating links into different types and using that information to help it calculate how changes should be handled so as quicker convergence can take place under much more stable network conditions.
Practical Benefits of RSTP
RSTP only builds upon the enhancements supplied by STP, which makes it faster due to 3 concepts:
Less waiting time during topology change means less network downtime, which = more network up-time.
Network Performance Enhancements: Faster Forwarding state and optimised BPDU handling lead to better network performance overall.
Port states and roles: Streamlined port states and roles for easier network management endif(Describe features here.)
Redundancy: a network with the capability to adjust on the fly for changes that have occurred by providing alternative paths (Figure 74) enhances system reliability and fault tolerance.
Conclusion
The Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) – one of the biggest improvements in networking technology, as RSTP overcomes limitations inherent to its predecessor: STPOriginally published on Kevin Glass blog. RSTP improved convergence times, reduced number of port states to simplify the protocol operation and message processing, faster BPDU handling engineered into real operation at a consistent time for sub second or few seconds timers in all scenarios beyond edge switch ports, fast transition from learning state L2/L1/Alternative /Disabled until forwarding status would be en-acted within last millisecond which. RSTP is a must-know for network administrators and IT personnel needing to get the most out of contemporary networking infrastructures guaranteeing maximum connectivity. Adopting RSTP not only reduces your downtime, but it helps you in the long run creating more fault tolerant and better functioning networks for a growing connecting world.