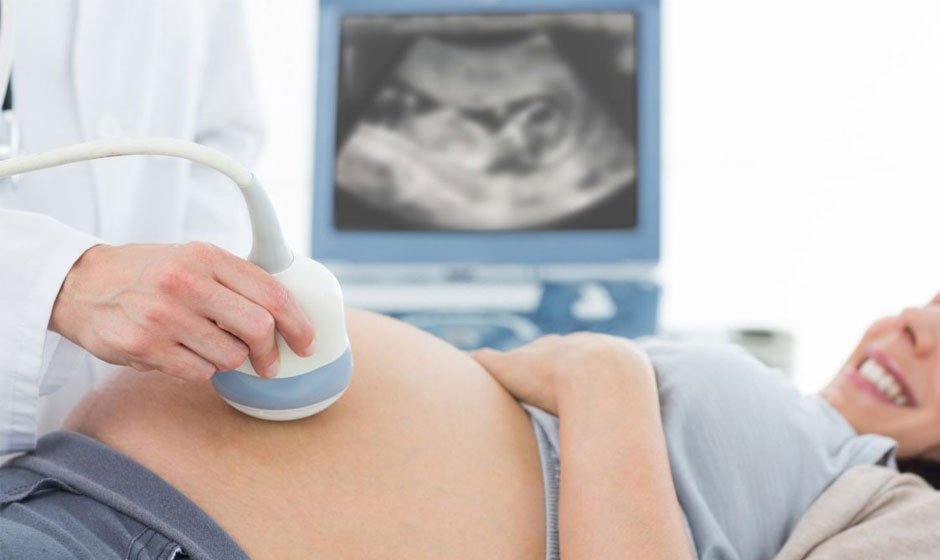
Pregnancy ultrasound has revolutionized prenatal care, offering invaluable insights into fetal development and maternal health. This non-invasive imaging technique has become a cornerstone of obstetrics, providing expectant parents and healthcare providers with crucial information throughout the gestational period. We’ll delve into the intricacies of pregnancy ultrasound and explore its diverse applications and benefits. You can schedule a pregnancy ultrasound in Oregon City.
Unveiling the Depths of Pregnancy Ultrasound: Applications, Benefits, and Beyond
1. The Evolution of Ultrasound Technology
Ultrasound technology has rapidly evolved since its inception in the mid-20th century. Initially used for naval and industrial purposes, ultrasound found its medical application in the 1950s, paving the way for obstetric ultrasound by the 1960s. Early ultrasound machines produced low-resolution images, but advances in transducer technology, signal processing, and imaging algorithms have led to high-definition 2D, 3D, and even 4D ultrasound imaging, enhancing diagnostic capabilities and fetal visualization.
2. Types of Pregnancy Ultrasound
- Transabdominal Ultrasound (TAU)
Transabdominal ultrasound is a common modality in which a transducer is moved over the abdomen after a gel is applied to facilitate sound wave transmission. This method is effective for early pregnancy dating, assessing fetal growth and placental location, and detecting abnormalities like cysts or tumors. - Transvaginal Ultrasound (TVU)
Transvaginal ultrasound involves inserting a probe into the vagina for closer proximity to the uterus and early gestational sac visualization. It offers higher resolution and is often used in early pregnancy to confirm viability, detect ectopic pregnancies, or evaluate the cervix and pelvic organs. - Doppler Ultrasound
Doppler ultrasound assesses blood flow using sound waves, aiding in evaluating fetal well-being by assessing umbilical and uterine blood flow. It’s crucial in managing high-risk pregnancies, identifying conditions like intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), and monitoring placental function.
3. Clinical Applications of Pregnancy Ultrasound
- Confirming Pregnancy and Gestational Age
One of the primary uses of ultrasound in early pregnancy is confirming intrauterine pregnancy, ruling out ectopic or molar pregnancies. It accurately determines gestational age by measuring crown-rump length (CRL) in the first trimester or biparietal diameter (BPD) and femur length in subsequent trimesters. - Assessing Fetal Growth and Anatomy
Ultrasound monitors fetal growth throughout pregnancy, ensuring appropriate development and detecting anomalies like neural tube defects, cardiac abnormalities, or cleft lip/palate. Anomaly scans in the second trimester provide a comprehensive assessment of fetal anatomy. - Monitoring High-Risk Pregnancies
Ultrasound plays a crucial role in managing high-risk pregnancies, including those with maternal diabetes, hypertension, or fetal genetic disorders. It helps monitor fetal growth, assess amniotic fluid levels, and detect signs of distress or abnormalities requiring intervention.
4. Advantages of Pregnancy Ultrasound
- Non-invasive and safe: Ultrasound poses minimal risk to both mother and fetus, making it a safe imaging modality during pregnancy.
- Real-time imaging: Provides immediate visual feedback, aiding in quick diagnosis and decision-making.
- Emotional bonding: Allows parents to visualize their unborn child, fostering emotional attachment and parental involvement.
5. Limitations of Pregnancy Ultrasound
- Operator-dependent: Skill and experience influence image quality and diagnostic accuracy, emphasizing the need for trained sonographers.
- Limited penetration: Obesity or fetal positioning can hinder image clarity, necessitating alternative approaches or repeat scans.
- Interpretation challenges: Complex anomalies or subtle abnormalities may require specialized expertise for accurate diagnosis and counseling.
6. Ethical Considerations and Controversies
The widespread use of pregnancy ultrasound has raised ethical considerations and controversies, including concerns about overutilization leading to unnecessary interventions or anxiety. Some argued against non-medical “keepsake” ultrasounds, emphasizing the importance of medical necessity and informed decision-making regarding ultrasound frequency and indications.
7. Future Trends and Innovations
The future of pregnancy ultrasound holds promising advancements, including:
- AI-Assisted Imaging: Artificial intelligence algorithms can enhance image quality, automate measurements, and aid in anomaly detection, improving diagnostic accuracy and efficiency.
- Fetal MRI Fusion: Combining ultrasound with fetal MRI data enables multi-modal imaging, enhancing diagnostic capabilities for complex fetal anomalies.
- Portable Ultrasound Devices: Miniaturized ultrasound devices offer point-of-care imaging, which is particularly beneficial in resource-limited settings or remote areas lacking access to comprehensive medical facilities.
8. Impact on Maternal and Fetal Health
Pregnancy ultrasound significantly impacts maternal and fetal health by enabling early detection of potential complications. For instance, it aids in diagnosing placenta previa, a condition where the placenta partially or fully covers the cervix. This condition can lead to bleeding during pregnancy and necessitate careful management to prevent adverse outcomes. Additionally, ultrasound helps identify conditions like polyhydramnios (excessive amniotic fluid) or oligohydramnios (low amniotic fluid), guiding interventions to optimize pregnancy outcomes and reduce risks for both mother and baby.
9. Psychological Benefits for Parents
Beyond its clinical utility, pregnancy ultrasound offers profound psychological benefits for expectant parents. Seeing their baby’s images on the screen fosters a deep emotional connection and sense of anticipation, promoting parental bonding and nurturing. This visual confirmation of pregnancy and the ability to observe fetal movements and features contribute to a positive pregnancy experience, easing anxieties and strengthening the parental-child relationship even before birth.
10. Educational and Research Opportunities
Ultrasound in pregnancy is also a valuable educational tool for healthcare professionals and researchers. It provides insights into fetal development, anatomical variations, and pathologies, facilitating medical education and advancing scientific knowledge. Moreover, ultrasound findings contribute to ongoing research in obstetrics, helping elucidate factors influencing fetal growth, developmental milestones, and the impact of interventions, leading to continuous improvements in prenatal care and outcomes.
Pregnancy ultrasound is a cornerstone of modern obstetrics, revolutionizing prenatal care and enhancing fetal and maternal outcomes. Its diverse applications, from confirming pregnancy to monitoring high-risk cases, highlight its indispensable role in healthcare. As technology advances, ultrasound’s potential for improving diagnostic accuracy and patient care remains boundless, ushering in a new era of prenatal imaging and healthcare innovation.